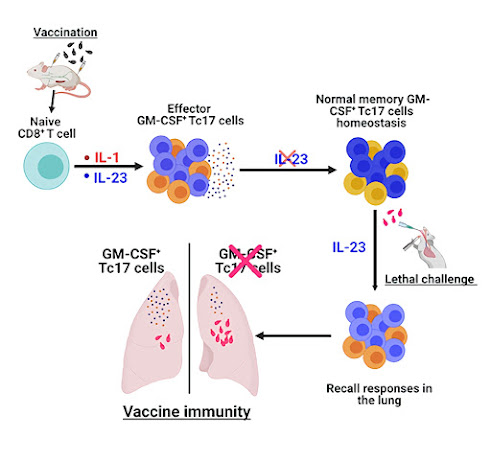
Researchers at the University of Illinois College of Veterinary Medicine have demonstrated in a mouse model that a specific type of T cell, one of the body’s potent immune defenses, produces cytokines that are necessary for the body to acquire immunity against fungal pathogens. This finding could be instrumental in developing novel, effective fungal vaccines.
Despite vaccines being hailed as one of the greatest achievements of medicine, responsible for controlling or eradicating numerous life-threatening infectious diseases, no vaccines have been licensed to prevent or control human fungal infections.
This lack proved especially deadly during the COVID-19 pandemic. In countries where steroids were widely used to suppress inflammation of the lungs, COVID-19 patients with preexisting conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes showed a greater likelihood of developing lethal fungal infections.



.jpg)




.jpg)







.jpg)