 |
| Photo Credit: Filipe Almeida |
Discovery of a gene in multiple mammalian species could pave the way for a highly effective, reversible and non-hormonal male contraceptive for humans and animals.
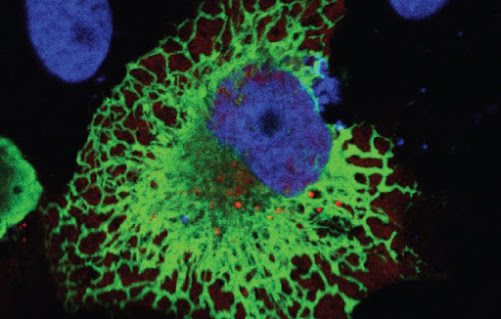
Washington State University researchers identified expression of the gene, Arrdc5, in the testicular tissue of mice, pigs, cattle and humans. When they knocked out the gene in mice, it created infertility only in the males, impacting their sperm count, movement and shape. The researchers detailed their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
“The study identifies this gene for the first time as being expressed only in testicular tissue, nowhere else in the body, and it’s expressed by multiple mammalian species,” said Jon Oatley, senior author and professor in WSU’s School of Molecular Biosciences. “When this gene is inactivated or inhibited in males, they make sperm that cannot fertilize an egg, and that’s a prime target for male contraceptive development.”
While other molecular targets have been identified for potential male contraceptive development, the Arrdc5 gene is specific to the male testes and found in multiple species. Importantly, lack of the gene also causes significant infertility creating a condition called oligoasthenoteratospermia or OAT. This condition, the most common diagnosis for human male infertility, shows a decrease in the amount of sperm produced, slowed mobility and distorted shape so that the sperm are unable to fuse with an egg.

.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
