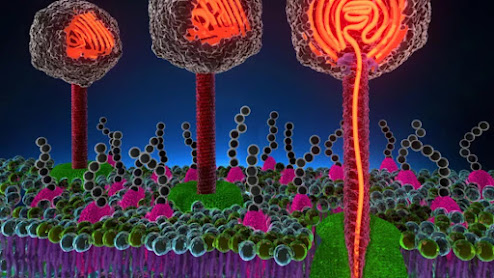
A research team in Japan, led by Nagoya University’s Akira Yokoi, has developed an innovative technique using cellulose nanofiber (CNF) sheets derived from wood cellulose to capture extracellular vesicles (EVs) from fluid samples and even organs during surgery. EVs are small structures from cancerous cells that play a crucial role in cell-to-cell communication. Extracting and analyzing EVs using this new technology has the potential to revolutionize early cancer diagnosis and open the door to personalized medicine. The researchers published their findings in Nature Communications.
Cancer is notorious for its poor prognosis and in many cases goes undetected until its advanced stages, leaving patients with limited treatment options. Detecting the cancer early using EVs and analyzing them provides vital information on disease status and its progression. This should assist physicians in monitoring and adjusting personalized cancer treatment plans. However, researchers have been limited in previous attempts to use EVs due to the lack of an effective isolation strategy.



.jpg)





.jpg)






.jpg)